Table of Contents
- Introduction to Ohm’s Law
- The History Behind Ohm’s Law
- Ohm’s Law Formula & Calculations
- Practical Applications of Ohm’s Law
- Limitations & Exceptions
- Advanced Concepts
- FAQs
1. Introduction to Ohm’s Law
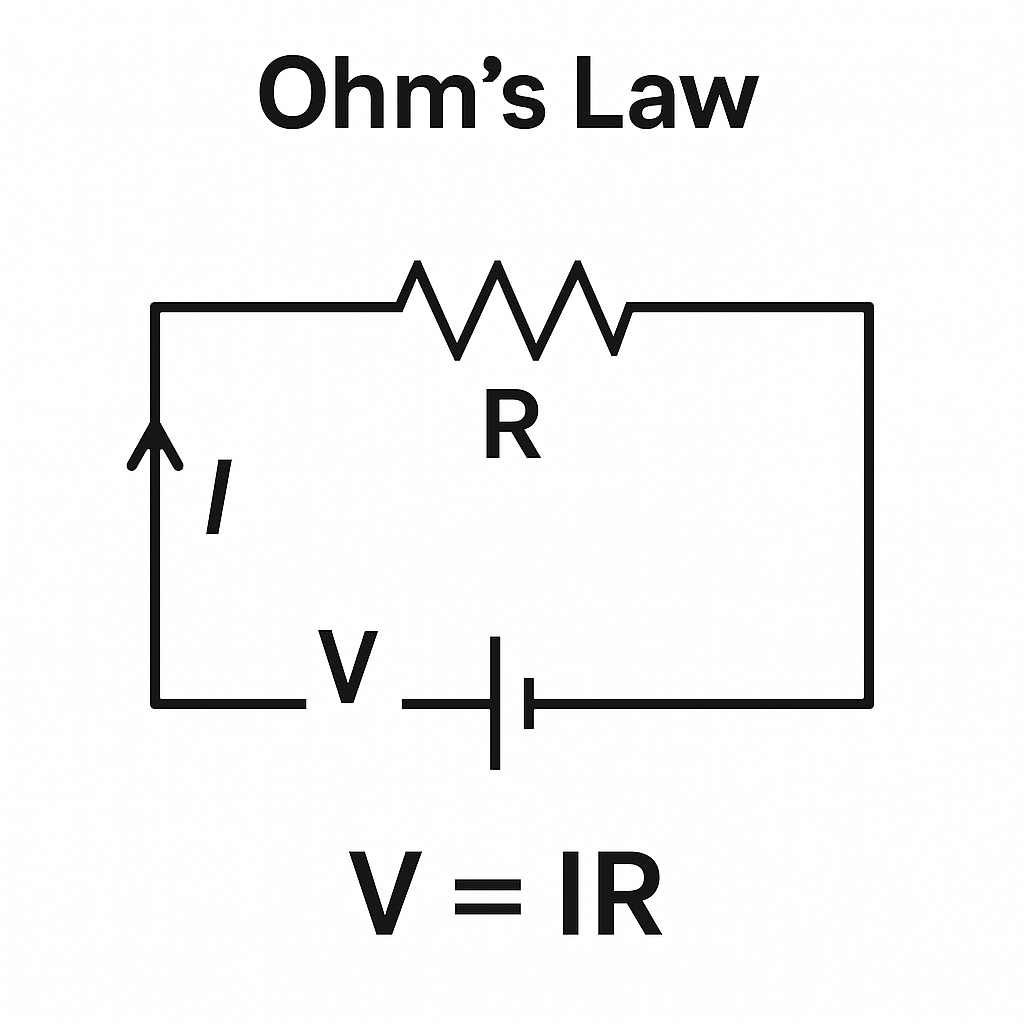
Ohm’s Law is the fundamental principle that governs electrical circuits. Established by Georg Ohm in 1827, this law defines the exact relationship between three key electrical properties:
- Voltage (V): The electrical potential difference (measured in Volts)
- Current (I): The flow of electrical charge (measured in Amperes)
- Resistance (R): The opposition to current flow (measured in Ohms)
The core Ohm’s Law formula is:
V = I × R
This simple equation allows engineers to:
✔ Calculate unknown values in circuits
✔ Design efficient electrical systems
✔ Troubleshoot common electrical problems
2. The History Behind Ohm’s Law
The discovery of Ohm’s Law was a revolutionary moment in electrical engineering:
1827: German physicist Georg Simon Ohm publishes his findings after extensive experiments with different conductors
Initial Resistance: The scientific community initially rejected his work
Final Acceptance: By the 1840s, the importance of his discovery was universally recognized
Key experiments involved:
- Measuring current through wires of different lengths
- Testing various conductive materials
- Developing the mathematical relationship we now know as Ohm’s Law
3. Ohm’s Law Formula & Calculations
The standard Ohm’s Law formula can be rearranged to solve for any variable:
| Calculation | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Find Voltage | V = I × R | 2A × 10Ω = 20V |
| Find Current | I = V ÷ R | 12V ÷ 4Ω = 3A |
| Find Resistance | R = V ÷ I | 9V ÷ 3A = 3Ω |
Real-World Application:
If you have a 12V car battery connected to a 6Ω headlight:
Current (I) = 12V ÷ 6Ω = 2A
4. Practical Applications of Ohm’s Law
Ohm’s Law is used daily in:
Circuit Design:
- Selecting appropriate resistor values
- Determining power supply requirements
Troubleshooting:
- Diagnosing short circuits
- Identifying faulty components
Power Management:
- Calculating heat dissipation (P = V × I)
- Preventing component overload
5. Limitations & Exceptions
While Ohm’s Law applies to most conductive materials, there are important exceptions:
Non-Ohmic Devices:
- Diodes
- Transistors
- LEDs
Special Cases:
- Superconductors (zero resistance)
- Semiconductors (variable resistance)
6. Advanced Concepts
For those ready to go beyond basics:
AC Circuits:
Ohm’s Law applies, but impedance (Z) replaces resistance
Power Calculations:
P = V × I = I² × R = V² ÷ R
Kirchhoff’s Laws:
Builds on Ohm’s Law for complex circuit analysis
Ohm’s Law Practice Problems with Solutions
Basic Problems (Single Variable Calculations)
- Problem: Find voltage when I = 3A and R = 4Ω
Solution: V = I × R = 3 × 4 = 12V - Problem: Calculate current when V = 9V and R = 3Ω
Solution: I = V/R = 9/3 = 3A - Problem: Determine resistance when V = 24V and I = 6A
Solution: R = V/I = 24/6 = 4Ω
Intermediate Problems (Power Calculations)
- Problem: Find power when V = 5V and I = 2A
Solution: P = V × I = 5 × 2 = 10W - Problem: Calculate current when P = 100W and R = 25Ω
Solution: I = √(P/R) = √(100/25) = 2A
Series Circuit Problems
- Problem: Two resistors (2Ω and 3Ω) in series with 10V supply. Find total current.
Solution: R_total = 2+3 = 5Ω → I = 10/5 = 2A
Parallel Circuit Problems
- Problem: Two 4Ω resistors in parallel with 12V supply. Find total current.
Solution: R_total = (4×4)/(4+4) = 2Ω → I = 12/2 = 6A
Challenge Problems
- Problem: A 1.5kW heater operates at 120V. What’s its resistance?
Solution: R = V²/P = (120×120)/1500 = 9.6Ω
7. Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Why is Ohm’s Law important?
A: It’s the foundation for understanding all electrical systems
Q: Can Ohm’s Law fail?
A: Only in non-ohmic materials where resistance isn’t constant
Q: How is Ohm’s Law used in real life?
A: From designing smartphones to maintaining power grids
Q: Can Ohm’s Law be used for all materials?
A: No – only for “ohmic” materials where resistance stays constant
Q: How accurate is Ohm’s Law in real circuits?
A: Extremely accurate for simple DC circuits with metal conductors
Q: Why do we need practice problems?
A: Solving problems builds intuition for real-world circuit analysis
Conclusion
Mastering Ohm’s Law is essential for anyone working with electricity. This fundamental principle connects voltage, current and resistance in a way that powers our modern world.
🔗 Recommended Resources:
📢 Enjoyed this guide? Share it and visit CodeEngine.Live for more electrical engineering content!
